The architectural, engineering and construction domain is fast evolving. With technologies like BIM acquiring a center stage, many industry professionals and stakeholders get confused about all the terms and jargon they keep on hearing.
In this blog, let’s look at some industry-specific terminology and special BIM terms you should know before you jump deeper into the world of Building Information Modeling (BIM).
No worries. Let us send you a copy so you can read it when it’s convenient for you. Just let us know where to send it.
1.
3D Modeling
3D modeling is the most common form of BIM that uses a common data environment to create and share graphic/non-graphic information in a 3D model for collaboration.
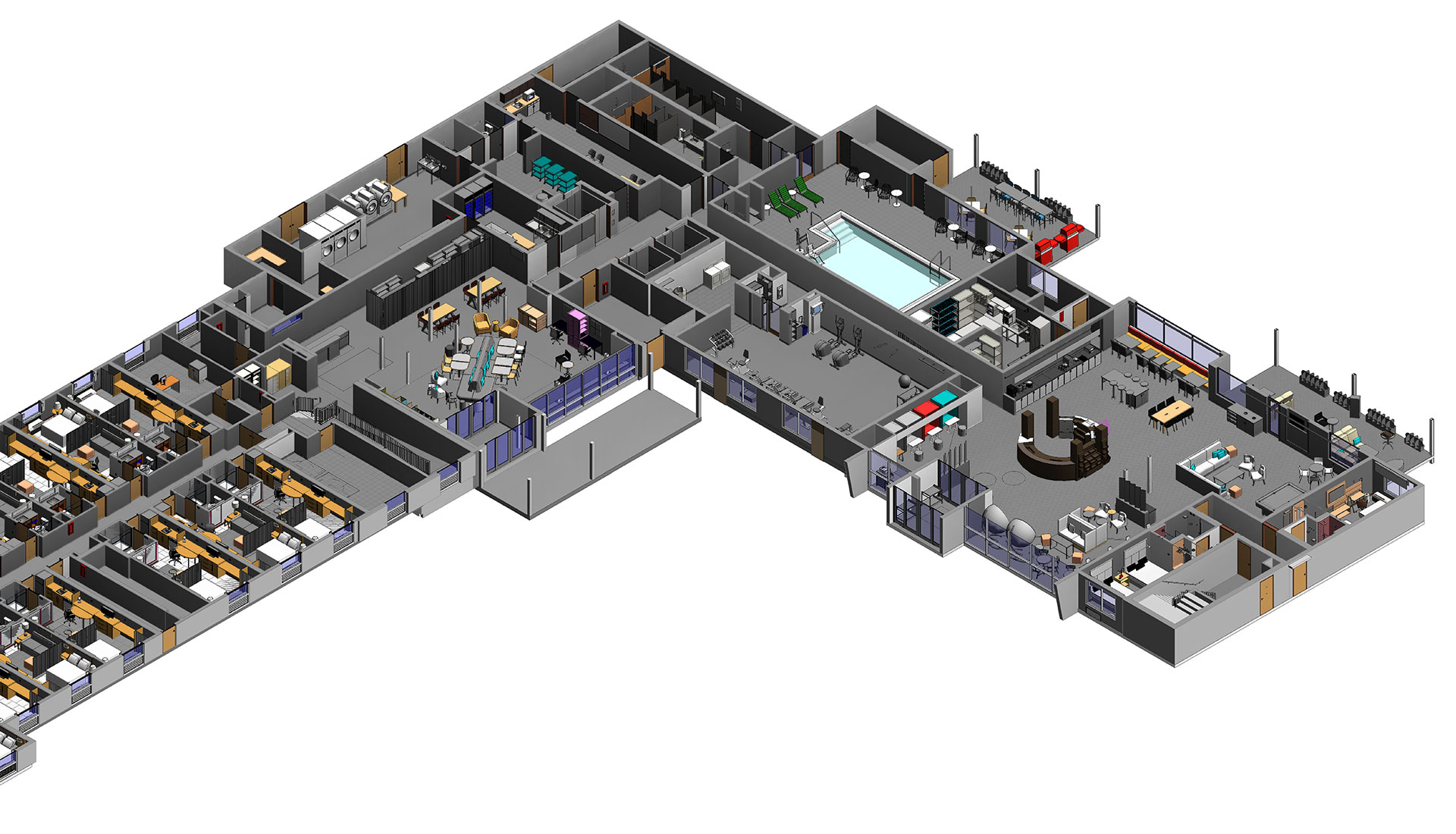

2.
4D Modeling
4D modeling adds construction sequencing information in the project model that lets stakeholders know how the project will be developed sequentially. Essentially, this involves adding scheduling data to the components to keep everyone informed on the development sequence.
3.
5D Modeling
5D modeling is related to cost information and enriches a BIM model with accurate cost information associated with various components and systems. 5D model embeds capital costs, operational costs and replacement costs associated with every physical aspect of a project. The calculation is linked to different components within the graphic model itself.
Read this detailed article about BIM Dimensions at,
What are BIM Dimensions- 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D and 7D BIM Explained | Definition & Benefits
4.
Asset Information Model
An asset information model is essentially a BIM model complemented with all the required information essential to operate and manage the asset after construction. An asset can refer to civil or infrastructure work or any other dedicated asset within the bigger BIM model.
5.
Building Information Model
A building information model (BIM) is a digital depiction or representation of various components of a building or facility, usually in a 3D format. The three-dimensional model is linked to a central database consisting of information about materials, components, systems, products and their attributes.
6.
Building Information Modeling
Building information modeling is the process of creating informative 3D models using data modeling software. This is done to create a detailed representation of a building digitally to outline the physical and functional attributes.
7.
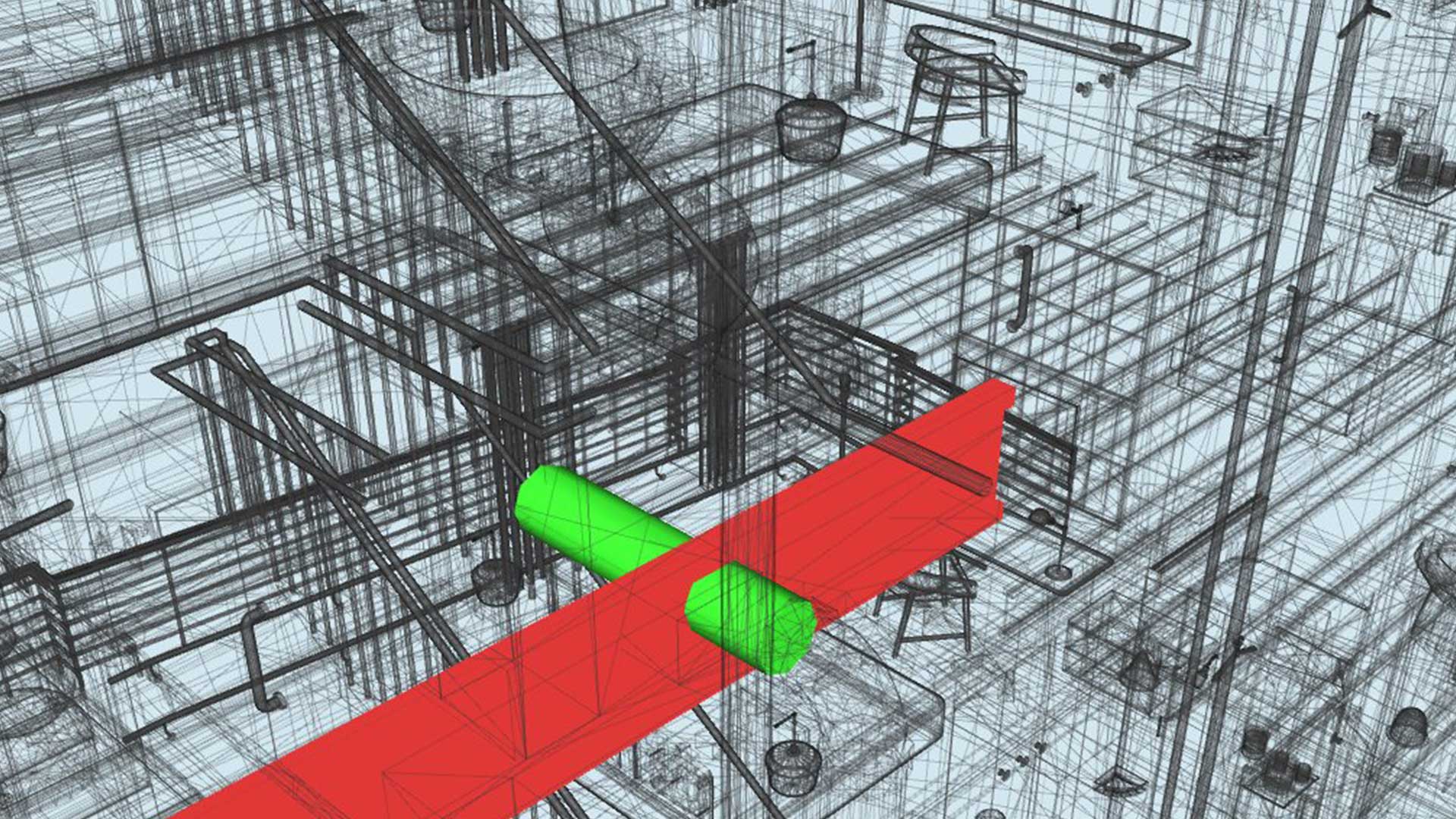
BIM Coordination (Clash Detection)
BIM coordination allows various stakeholders to work with each other throughout the entire lifecycle of a BIM project. This is done to avoid chances of clashes and detect the same at early stages to minimize wastage of resources and for achieving cost-efficiency. Clash detection helps discover conflicts between various elements- structural, MEP through a digital approach via the BIM model.
Feel free to explore this article,
How clash detection is augmenting construction drawing validation?
8.
BIM Levels
BIM works on different levels from Level 0 to level 3 where Level 0 means making use of 2D CAD drafting with no collaboration. BIM levels can be said to be distinct milestones that take the modeling process to greater collaboration. The distinct levels are as follows:
- Level 0: 2D CAD drafting with no collaboration between stakeholders
- Level 1: Amalgamation of 3D CAD and 2D for documentation and product information. The data is shared electronically through a CDE. Though there is no collaboration between various stakeholders. Each maintains its own data.
- Level 2: Collaborative working using 3D CAD models where information is shared via a common file format.
- Level 3: Complete integration of work between all the stakeholders using the shared project model stored in a common data environment to eliminate conflicts.
Feel free to explore them in detail at,
BIM Maturity Levels Explained- Level 0, Level 1, Level 2, Level 3
9.
BOQ (Bill of Quantities)
A Bill of Quantities is developed by a cost consultant or quantity surveyor to provide accurate quantities of the materials, parts, etc. required for completing a task by looking at the drawings or specifications.
10.
BOM (Bill of Material)
A Bill of materials is used to enlist the raw materials, parts, components, sub-components required for completing a project.
Related article:
What is BOQ & BOM and How BIM is Improving BOQ/BOM Development Process?
11.
BIM Objects
A BIM object contains detail information about a component and its geometry representing its physical characteristics within a project model.
Are you looking to develop custom BIM objects library, check out our,
Revit family creation service.
12.
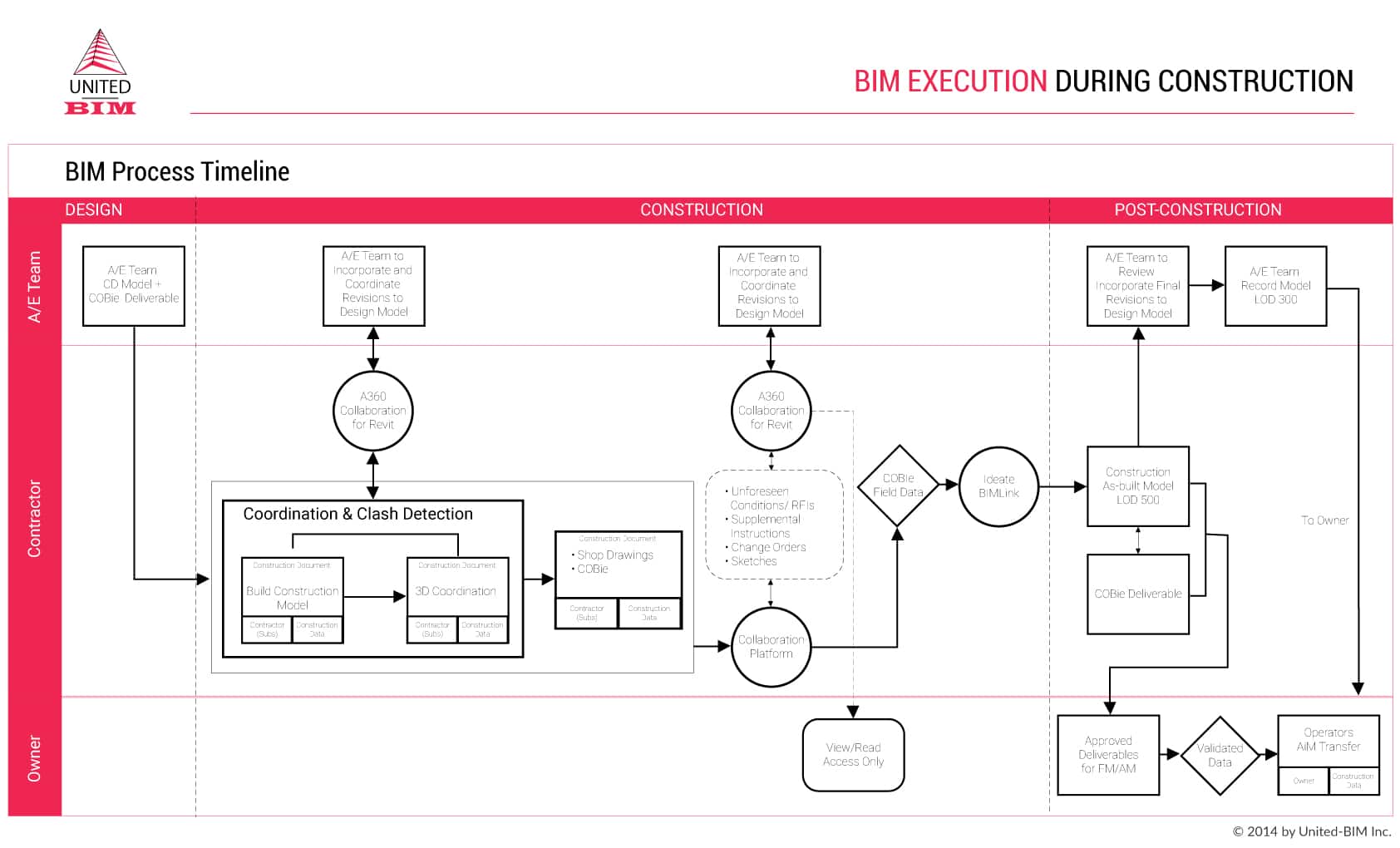
BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
A BIM execution plan is drafted to manage project delivery. BEP is categorized into pre-contract and post-contract BEP where pre-contract BEP outlines the proposal in response to the information requirements and post-contract BEP consists of delivery details.
Here is everything you need to know about BIM Execution Plan,
BIM Execution Plan (BXP)- What, Why, When and How
13.
BS 1192
The term is a code of practice used for referring the process of producing AEC information, collaboratively in conjunction with each other.
14.
BS 1192-4
The standard term used to refer to the collaborative information drafting associated with fulfilling the employer’s information exchange requirement using COBie.
15.
Common Data Environment (CDE)
Common Data Environment (CDE) is a shareable information repository that can be used by all the stakeholders in a BIM project. All the data related to a BIM model is created, stored and shared via the CDE through cloud storage that can be accessed by various departments/stakeholders to improve coordination and boost productivity.
16.
CIC BIM Protocol
A standard legal agreement prepared for construction and contractor clients outlining additional rights and duties of the employer and contracted parties for promoting collaborative working without diluting ownership and control over intellectual property.
17.
Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie)
A comprehensive data scheme consisting of a portion of information within the building model created for facility management handover.
Read the full article about COBie, the standard information exchange system for BIM at,
What Is COBie & How It Streamlines Data Collaboration Between AEC Professionals
18.
Clash Rendition
Clash rendition is the process undertaken to minimize chances of clashes and speed up the process of clash detection between Building Information Models (BIM) developed by different teams. Clash rendition is done to reduce errors and minimize costs.
19.
Data Exchange Specification
Data exchange specification is a standard specification for electronic file formats for facilitating the exchange of digital data between various BIM software to promote interoperability.
20.
Federated Model
A federated model is an integrated model developed by collating different individual models into a single model. This is done by importing several models into a single model via the process of collaborative working.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
* We don’t share your personal info with anyone. Check out our Privacy Policy for more information.
21.
IFC specification
IFC specification is a data standard managed by buildingSMART international that governs the data format for describing, sharing and exchanging information used in the building and facility management sector. Fundamentally, it includes definition, schemas, and libraries of IFC- a neutral data format.
22.
Information Delivery Manual
An information delivery manual is developed to identify different construction processes and articulate information required at every stage. IDM is developed using a standard format outlined in ISO 29381-1. The information delivery manual is designed to make the required information available to stakeholders whenever required.
23.
Life-cycle Assessment(LCA)
Life-cycle assessment or life cycle analysis is the process of determining the environmental impact of any project – all its assets in terms of materials consumed, energy expended and waste/pollutants released during its entire lifecycle. Fundamentally, LCA is done to check an environmental load of an asset using a standard methodology defined in ISO 14040.
24.
Level of Detail
Level of detail is a standard defined in PAS 1192-2 which depicts the Level of Model Detail and Level of Information Detail. While the level of model detail outlines the graphical content on models at each stage, the level of model information is associated with non-graphical content within models at different stages. Level of detail can be schematic, conceptual or defined.
25.
LOD- Level of Development
Level of Development (LOD) specification allows AEC professionals to articulate Building Information Models at different stages of the design and construction process. It is a form of a standard reference that promotes clarity, accuracy, and reliability of the content of a BIM model.
Read the detailed article about LOD definitions and how each level represents the capability of a BIM model at,
BIM Level of Development | LOD 100, 200, 300, 350, 400, 500
26.
Open BIM
Open BIM is an open-source version of a collaborative design, development and building operations using open standards and frameworks. Build using the SMART data model, open BIM incorporates data to ISO 16739, processes to ISO 29381-1 and terms to ISO 12006-3.
27.
Quantity Take-off
Quantity take-offs refer to an accurate measurement of materials and labor required for completing a construction project. An estimator develops quantity-takeoffs during the pre-construction process which are used for outlining the scope of construction.
28.
PAS 1192
PAS 1192 framework outlines the level of model detail in terms of graphical content, model information in terms of specification data and model definition in terms of meaning is required. Also, its subsets, PAS 1192-2, PAS 1192-3, PAS 1192-5 and BS 1192-4 defines how much information is required for various stages such as CAPEX, OPEX, etc
29.
Record BIM
Record BIM refers to a coordinated model or a group of models that represents the construction of a structure completed under a contract. It is submitted by a contractor or subcontractor.
30.
Uniclass
Uniclass is a standard classification system used in the United Kingdom which allows grouping of objects into numerical headers. This facilitates a streamlined arrangement of information as per type or class and is used for categorization within BIM models.
Wrapping Up
So, that’s it. Here are a lot of terms you should be prevalent in if you are thinking of using BIM for your next project. Though the list is comprehensive, but not entirely exhaustive. Feel free to share more terms with us or get in touch with our experts to understand a specific term and its implication for your architectural, engineering or construction project.