Last updated on: January 10, 2025
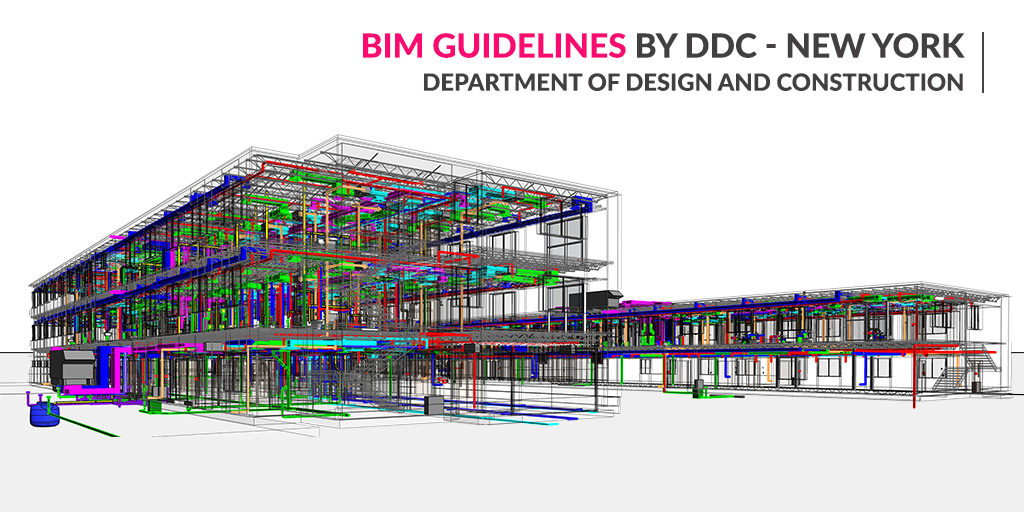
The BIM uses guidelines by the New York-DDC (Department of Design & Construction) state the consistent use of BIM across a wide range of building types and municipal agencies. This guide is about utilizing BIM and ensuring uniformity in the use of BIM for all the public building projects in New York City. The information in BIM and digitization of building information will enhance buildings project from conceptual design to operations & maintenance and on to demolition or renovation.
DDC-New York BIM Guidelines state that BIM authoring software shall be used through the project life cycles, supporting design criteria, pre-preliminary design, schematic design, design development, final construction documents, bid award and registration, construction, and regulatory approvals.
BIM use Advantages
- Instant 3D Visualization of 2D drawings/objects
- Enhance the coordination process by effectively detecting and solving clashes at the initial stage before they lead to outrageous change orders
- Demonstrate timely construction schedules (4D BIM) and site operations
- Connect cost factors to the 3D model or components for efficient estimation and a transparent bidding process
- Provide advanced models to the clients or facility managers for further use in building maintenance and operations
BIM use Software
With BIM tools and software, the designs can be created directly in 3D as an assortment of model components (like the lines, circular arcs, and blocks in a 2D CAD drawing). As the project progresses, more intelligence is added to the model, and this knowledge is captured in an information base.
The following table shows a list of current known and acceptable BIM authoring software for DDC Projects:
| BIM Use | BIM Use Software |
|---|---|
| Space Programming | Trelligence Afinnity Programming, Onuma System, dRofus Smart Planning |
| Architectural Design | Autodesk Revit Architecture, Bentley Architecture, Graphisoft ArchiCAD, Nemetschek Vectorworks Architect |
| Structural Design | Autodesk Revit Structure, Tekla Structures, Bentley Structural Modeler |
| Inter-Disciplinary Coordination and Clash Detection | Navisworks Manage, Solibri Model Checker |
| Code Checking | Solibri Model Checker |

Don’t have the time to read the whole blog, no worries you can download it and read it at your convenient time.
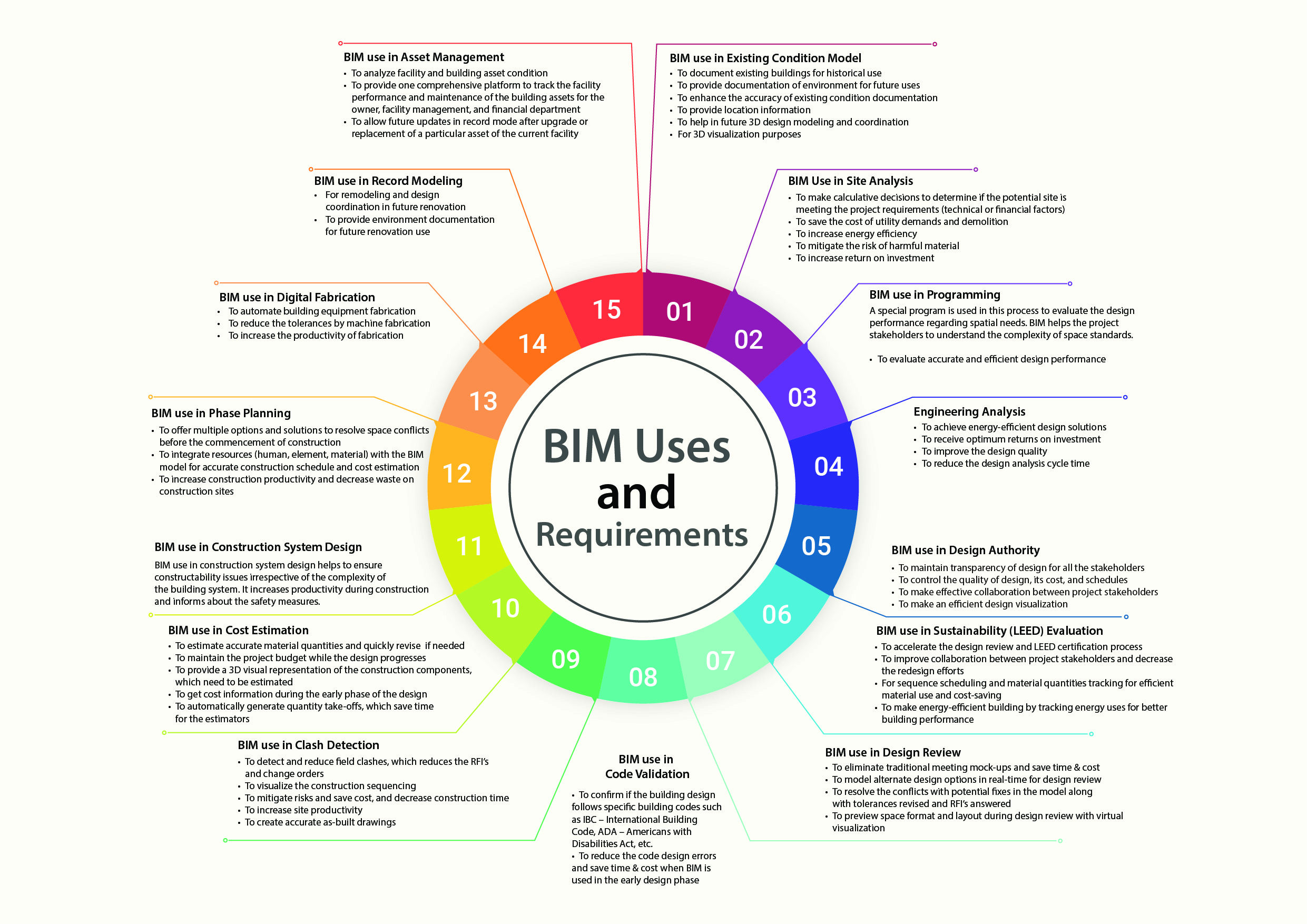
BIM Uses and Requirements on DDC Projects
1. BIM use in Existing Condition Model
It is a process in which a project team develops a 3D model of an existing building. The laser scanning technology is used to capture the existing conditions of a building (interiors, exteriors, landscape). Consultants using this technology are responsible for gathering the scanning data (point cloud data) and inserting it into BIM.
The value of BIM use in Existing Conditions Modeling is:
- To document existing buildings for historical use
- To provide documentation of environment for future uses
- To enhance the accuracy of existing condition documentation
- To provide location information
- To help in future 3D design modeling and coordination
- For 3D visualization purposes
2. BIM Use in Site Analysis
BIM or GIS devices are utilized in this process to assess properties in a given region to decide the ideal site area for a future project. The site information gathered is used to initially choose the site and then for the position of the building.
The value of BIM use in Site Analysis is:
- To make calculative decisions to determine if the potential site is meeting the project requirements (technical or financial factors)
- To save the cost of utility demands and demolition
- To increase energy efficiency
- To mitigate the risk of harmful material
- To increase return on investment
3. BIM use in Programming
A special program is used in this process to evaluate the design performance regarding spatial needs. BIM helps the project stakeholders to understand the complexity of space standards.
The value of BIM use in Programming is:
- To evaluate accurate and efficient design performance
4. Engineering Analysis
BIM tools are used in this process to make engineering effective by developing the building system information based on the design specifications. The use of BIM and analysis tools can significantly improve the design of the building system and its energy consumption during the facility lifecycle.
The value of BIM use in Engineering Analysis is:
- To achieve energy-efficient design solutions
- To receive optimum returns on investment
- To improve the design quality
- To reduce the design analysis cycle time
Find More In-Depth Content: BIM for MEP/FP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing, Fire Protection) Designers
5. BIM use in Design Authority
3D model software are used in this process to develop the design model. Design authoring tools are an important step towards BIM and it’s a key to connecting the 3D model with design data such as properties, quantities, elements, cost, and schedules.
The value of BIM use in Design Authoring is:
- To maintain transparency of design for all the stakeholders
- To control the quality of design, its cost, and schedules
- To make effective collaboration between project stakeholders
- To make an efficient design visualization
6. BIM use in Sustainability (LEED) Evaluation
It is a process of evaluating the sustainable criteria in a project which refers to material, performance, or a process. With the use of BIM, sustainability evaluation can be applied across all the phases of design and construction. It can be most effective when it is done in the conceptual and planning and design phases and further applied in the construction and operation phases.
The value of BIM use in Sustainability (LEED) Evaluation is:
- To accelerate the design review and LEED certification process
- To improve collaboration between project stakeholders and decrease the redesign efforts
- For sequence scheduling and material quantities tracking for efficient material use and cost-saving
- To make energy-efficient building by tracking energy uses for better building performance
7. BIM use in Design Review
3D model visualization is used in this phase to evaluate the meeting criteria such as sightlines, ergonomics, layout, lighting, textures, security, and colors. 3D virtual representation and virtual mock-ups can be implemented with BIM to analyze the design and solve the design and constructability issues.
The value of BIM use in Design Review is:
- To eliminate traditional meeting mock-ups and save time & cost
- To model alternate design options in real-time for design review
- To resolve the conflicts with potential fixes in the model along with tolerances revised and RFI’s answered
- To preview space format and layout during design review with virtual visualization
8. BIM use in Code Validation
Code validation software is used in this process to match the BIM model parameters with project-specific codes.
The value of BIM use in Code Validation is:
- To confirm if the building design follows specific building codes such as IBC – International Building Code, ADA – Americans with Disabilities Act, etc.
- To reduce the code design errors and save time & cost when BIM is used in the early design phase
9. BIM use in Clash Detection
It is a process in which clash detection software Navisworks is used to detect the interdisciplinary clashes by comparing 3D models of the building systems. BIM use in clash detection eliminates the major clashes before actual construction starts.
The value of BIM use in Clash Detection is:
- To detect and reduce field clashes, which reduces the RFI’s and change orders
- To visualize the construction sequencing
- To mitigate risks and save cost, and decrease construction time
- To increase site productivity
- To create accurate as-built drawings
10. BIM use in Cost Estimation
The cost estimation process helps to generate accurate quantity take-offs and cost estimation early in the design phase. BIM use in this process potentially saves cost & time and avoids budget overrun. Designers see the cost effects of their changes with the help of BIM, which reduces the redesign work and project budgets.
The value of BIM use in Cost Estimation is:
- To estimate accurate material quantities and quickly revise if needed
- To maintain the project budget while the design progresses
- To provide a 3D visual representation of the construction components, which need to be estimated
- To get cost information during the early phase of the design
- To explore new design options within the budget
- To automatically generate quantity take-offs, which save time for the estimators
Related Blog: 5D BIM Implementation- Barriers & Benefits- Boon for Every Cost Estimators
11. BIM use in Construction System Design
BIM use in construction system design helps to ensure constructability issues irrespective of the complexity of the building system. It increases productivity during construction and informs about the safety measures.
12. BIM use in Phase Planning
A process where BIM is used to plan occupancy in a remodel, retrofit, expansion, or show the construction sequence and space prerequisites on a building site. 4D BIM modeling is an impactful visualization and communication process that provides a better understanding of the construction plan.
The value of BIM use in Phase Planning is:
- To offer multiple options and solutions to resolve space conflicts before the commencement of construction
- To integrate resources (human, element, material) with the BIM model for accurate construction schedule and cost estimation
- To increase construction productivity and decrease waste on construction sites
13. BIM use in Digital Fabrication
It uses a machine technology where the objects are prefabricated directly from the BIM model.
The value of BIM use in Digital Fabrication is:
- To automate building equipment fabrication
- To reduce the tolerances by machine fabrication
- To increase the productivity of fabrication
14. BIM use in Record Modeling
Record modeling portrays an accurate representation of an existing condition of the building, its assets, and its environment. It contains information related to the building’s architectural, structural, and MEP disciplines. Additional data like equipment and space planning systems may be required if the intent of use is for maintenance and operations.
The record model can store more information that contains the correct depiction of space with links, warranties, and maintenance history for all the building components. It also includes information linking pre-build specifications to as-built specifications.
The value of BIM use in Record Modeling is:
- For remodeling and design coordination in future renovation
- To provide environment documentation for future renovation use
15. BIM use in Asset Management
A process in which an organized management system will efficiently help in the maintenance and operation of a building and its assets. These assets include the physical facility, systems, surrounding environment, and equipment. The building assets information is available in a record model. Further, this information is also essential for asset management to determine the cost implication of maintaining, operating, upgrading, or changing building assets.
The value of BIM use in Asset Management is:
- To analyze facility and building asset condition
- To provide one comprehensive platform to track the facility performance and maintenance of the building assets for the owner, facility management, and financial department
- To allow future updates in record mode after upgrade or replacement of a particular asset of the current facility
Reference:
https://www1.nyc.gov/
Explore our BIM Services in New York & the New York metropolitan area and feel free to connect with us if your design and construction project requires BIM services.
Email: info@united-bim.com or call us at +1(860) 317-7105
About the Author

Coordination Manager / VDC Manager at United BIM
With over 10 years of experience in the AEC industry, Akash Patel is a seasoned Coordination Manager and VDC Manager at United BIM. His expertise lies in managing complex MEP-FP coordination projects and leveraging cutting-edge BIM technology to ensure seamless collaboration and precision. Akash is dedicated to delivering high-quality, detailed models that meet the demands of modern construction. He is passionate about optimizing workflows and driving innovation within the BIM field.