Last updated on: January 2, 2025
Our experience with COBie has shown how it bridges design, construction and building operations. Although COBie is widely known, only a few fully know it’s potential. Let’s explore how COBie and BIM work together, highlighting their importance in the smooth shift from design, and construction to building operations
Personal Experience:
Having extensively used BIM and COBie, I’ve witnessed firsthand its ability to enhance collaboration, streamline data exchange, and improve decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. It’s not just a standard; it’s a game-changer in the world of Virtual Design and Construction (VDC).
What is COBie?
COBie, or Construction Operations Building Information Exchange, is a standardized format for organizing and delivering information about a building’s components and systems. It acts as a digital bridge, connecting design, construction and operation phases by facilitating the exchange of crucial data.

Where is It Used And How is it Integrated With BIM?
COBie finds application across the entire AEC industry, seamlessly integrating with BIM processes. From design to construction, COBie ensures that information flows coherently, enhancing collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers.
How is It Used?
COBie organizes building details neatly in a structured format. This information bridge ensures smooth communication between design and construction, making valuable data easily available for operations and ongoing maintenance of the project.
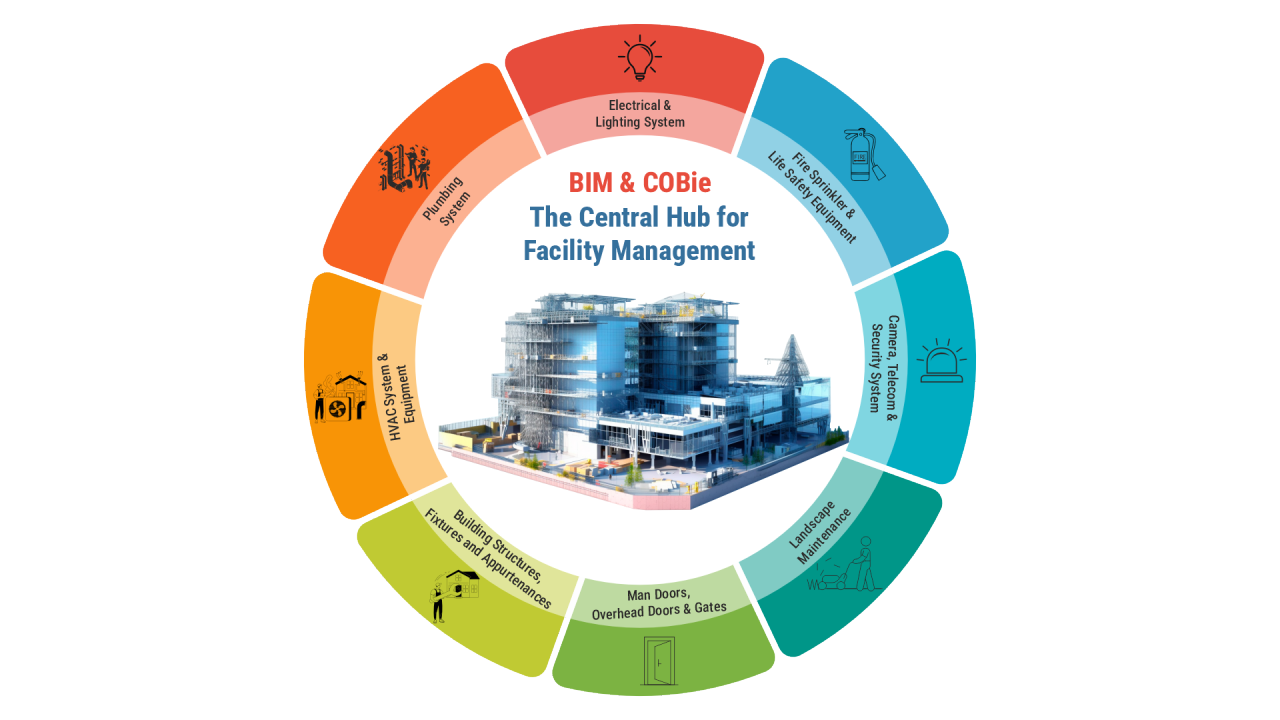
Components of COBie:
COBie data encompasses a wide range of information, including but not limited to:
Detailed information (like title, version, release, etc.) and instructions (about the facility, floor, space, zone, etc.) about the COBie file
Contact details of stakeholders involved in the project, ensuring effective communication and collaboration
Identification of the type of facility and other project details
Detail of number of floors/levels in the project
Includes information about the grouping and organization of spaces within a building like mechanical zone, common area, area A, area B, etc.
Details of individual equipment and components like plumbing fixtures, MEP-FP equipment, camera, furniture, door-windows and all COBie Asset Types of the entire property.
Level wise and room wise location of the individual components
Detailed information about building systems and equipment, such as HVAC, electrical, and plumbing, linked to specific spaces
Provides a breakdown of assemblies like Air Handling Unit, showing how individual components come together, offering insights into complex building structures
Data on how different building components are connected, aiding in the understanding of interdependencies
Details on attic stock (for future use) for building components, facilitating proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime
Details about the training and tools required to maintain and operate the facility, example – training and tools on how to operate the lighting systems, plumbing systems, fire alarm systems, etc.
Contains details on specific maintenance tasks and jobs related to building components like date for HVAC System Inspection, who is assigned the task, etc. – aiding in organized facility management and timely maintenance planning
Information on the potential environmental impact of a building component’s failure or maintenance on the overall system, supporting risk management
Links to relevant documents like specification sheets, details, etc. associated with each building component, aiding in comprehensive documentation
Additional attributes and characteristics of building components, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties, though this is not a mandatory field
Spatial coordinates of building components, facilitating accurate positioning and integration with other systems
Record of open issues during project handover
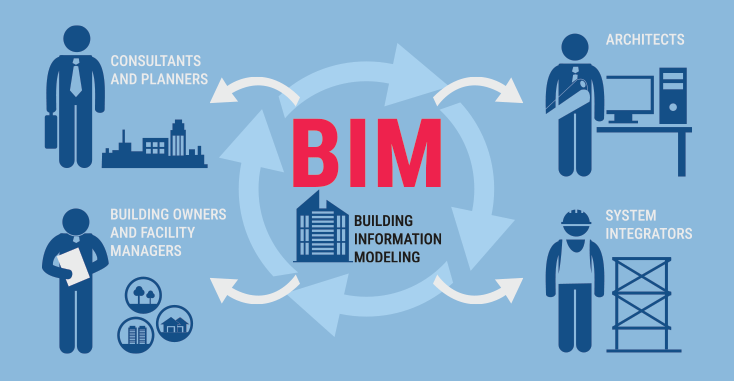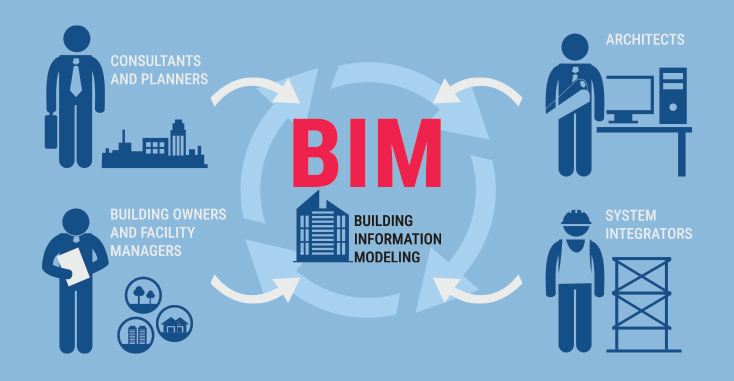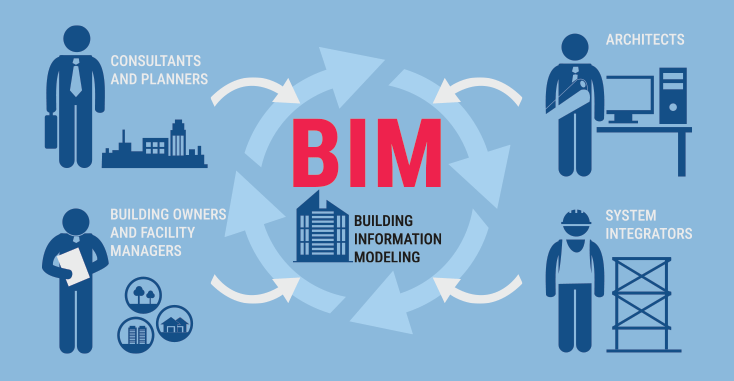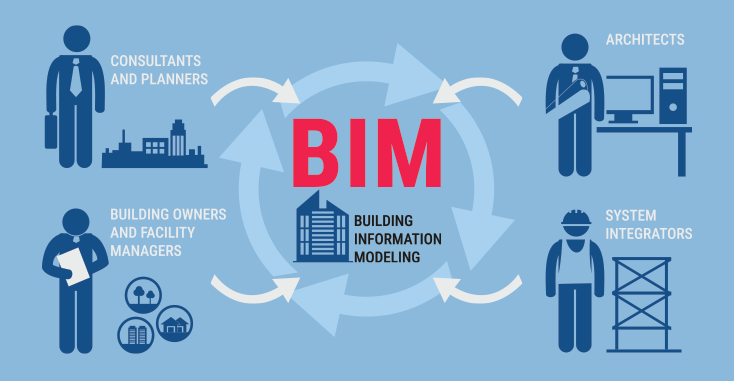
Who Benefits From COBie?
Several stakeholders in the construction and building management process can benefit from COBie:
Can use COBie to streamline the transfer of design information to construction and facility management
Benefit from COBie’s structured data for efficient collaboration and data exchange between design and construction phases
Use COBie to access accurate and standard information exchange system during construction, aiding in project coordination and quality assurance
Leverage COBie for comprehensive and organized data about building components, supporting efficient facility operations and maintenance.
Gain valuable insights into the building’s components and systems, facilitating informed decision-making regarding maintenance, renovations, or future projects
Use COBie data for day-to-day operations, ensuring effective management of spaces, systems, and maintenance activities
Can benefit from the structured information in COBie for strategic planning, asset tracking, and lifecycle management
Use COBie to ensure that building information is standardized and easily accessible for compliance checks and regulatory purposes
Employ COBie as part of the BIM process, ensuring data continuity and consistency throughout the project lifecycle
Utilize COBie for streamlined communication and data exchange between various project phases, enhancing project efficiency
Can access detailed information about their supplied components, aiding in inventory management and future product development
Rely on COBie data for effective planning and execution of maintenance activities, reducing downtime and enhancing facility performance
Conclusion:
COBie isn’t just a buzzword – it’s an essential tool in the BIM industry. By leveraging its capabilities, we can bridge the gap between design and construction, adopting a more efficient, collaborative, and informed approach to building projects. It’s time to not only recognize COBie’s importance but to ensure its correct implementation, unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology in our industry.
Dig further into How BIM is Facilitating Facility Management Process?
Yes, BIM and COBie integration can be applied to existing buildings through retroactive modeling, capturing the as-built conditions and generating the necessary facility management data for ongoing operations and maintenance.
While COBie is not mandatory in all projects, it is often required for government or public sector projects, especially in the United States and the UK, to ensure that building data is accessible for long-term maintenance and facility management.
While COBie is not mandatory in all projects, it is often required for government or public sector projects, especially in the United States and the UK, to ensure that building data is accessible for long-term maintenance and facility management.
Yes, COBie is applicable to both new construction projects and retrofits, ensuring that all essential building operation and maintenance data is captured for facility management purposes, regardless of when the building was built.
BIM creates detailed building models, while COBie organizes operational data for facility management. BIM and COBie integration ensures accurate, efficient data transfer for seamless handover, improving building maintenance and lifecycle management.
COBie is linked to the handover stage of construction, providing facility management data for operations and maintenance after project completion.
Yes, COBie is required for BIM Level 2 to ensure structured data handover for facility management at project completion.
About the Author

Coordination Manager / VDC Manager at United BIM
With over 10 years of experience in the AEC industry, Akash Patel is a seasoned Coordination Manager and VDC Manager at United BIM. His expertise lies in managing complex MEP-FP coordination projects and leveraging cutting-edge BIM technology to ensure seamless collaboration and precision. Akash is dedicated to delivering high-quality, detailed models that meet the demands of modern construction. He is passionate about optimizing workflows and driving innovation within the BIM field.