Last updated on: February 5, 2025
Airport construction optimization is increasingly powered by advanced technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), which has become essential to modern airport development. Given the complexity of airports, with systems spanning electrical, mechanical, and structural elements, traditional methods are no longer enough. The ability to create 3D digital models, supported by real-time data and collaborative tools, is proving to be a game changer in addressing the challenges of large-scale airport projects.
This blog will help you go through the transformative role of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in modern airport construction, highlighting its impact on efficiency, safety, cost savings, and sustainability. We cover key BIM applications such as streamlined coordination, clash detection, cost estimation, and sustainability, supported by real-world case studies from major airports like LAX, ORD, and SFO. The content demonstrates how it optimizes airport design, construction, and long-term operations, providing a comprehensive guide for airport developers seeking innovative, future-ready solutions.
How is BIM Modernizing Airport Construction?
Building Information Modeling (BIM Modeling and Coordination Services) has rapidly become an essential tool in the construction of airport projects. Airports, due to their large-scale and complex nature, require detailed coordination and cutting-edge technology to meet design, operational, and safety standards. With its ability to integrate information across all phases of design, construction, and operation, it is transforming the way airport projects are managed, ultimately providing greater efficiency, cost savings, and sustainability.
Why BIM is Crucial for Airports?
01.
Streamlined Coordination
BIM Modeling and Coordination Services excel in uniting complex airport systems into one cohesive model, ensuring seamless collaboration among designers, engineers and contractors. By incorporating clash coordination in BIM, potential conflicts between critical airport infrastructure systems—such as HVAC, electrical, and security—are identified before construction begins. This coordinated approach enhances efficiency and reduces costly delays in airport development.
02.
Boosted Efficiency & Fewer Errors
BIM allows for virtual simulation of the entire airport construction process, identifying potential issues early—such as design conflicts, system interferences, or safety risks. This proactive approach enhances efficiency, minimizes errors, and reduces costly delays, ensuring smoother project execution and timely delivery of airport infrastructure. By optimizing workflows, every step of the process is well-coordinated, ultimately streamlining the construction process and improving overall project outcomes.
03.
Accurate Cost Estimation & Efficient Planning
Building Information Modeling (BIM) facilitates accurate cost estimation and effective project planning, ensuring airports remain within budget. By visualizing the entire lifecycle, it identifies potential savings opportunities and helps prevent unexpected expenses. Additionally, collaborative project delivery enhances communication between all stakeholders, ensuring that financial management remains optimized.
04.
Enhanced Visualization for Stakeholders
The 3D models provide a comprehensive view of the entire airport project, enabling stakeholders to easily understand complex designs, ensure regulatory compliance, and monitor progress. This visual representation serves as a powerful communication tool, fostering better collaboration and decision-making throughout the construction process. Additionally, security systems integration allows stakeholders to assess and optimize security operations from the start.
05.
Sustainability & Environmental Benefits
Sustainable airport design relies on BIM advanced tools to simulate energy use, material efficiency, and waste reduction, helping achieve environmental goals. These tools also support ongoing sustainability efforts through lifecycle assessments, ensuring long-term operational savings. This approach is crucial for meeting green building certifications such as LEED.
06.
Operational Efficiency & Facility Management
Post-construction, BIM for facility management remains crucial for airport maintenance. It enables asset tracking, system performance monitoring, and scheduling preventative upkeep, ensuring seamless operations throughout the airport’s lifecycle. Integrating BIM into airport construction is not just a trend—it’s essential for modernizing projects, optimizing daily operations, and ensuring long-term success.
BIM is transforming the airport industry, not only by streamlining construction but also by optimizing long-term facility management, sustainability, and operational efficiency.
Key Technicalities Of BIM In Airport Projects
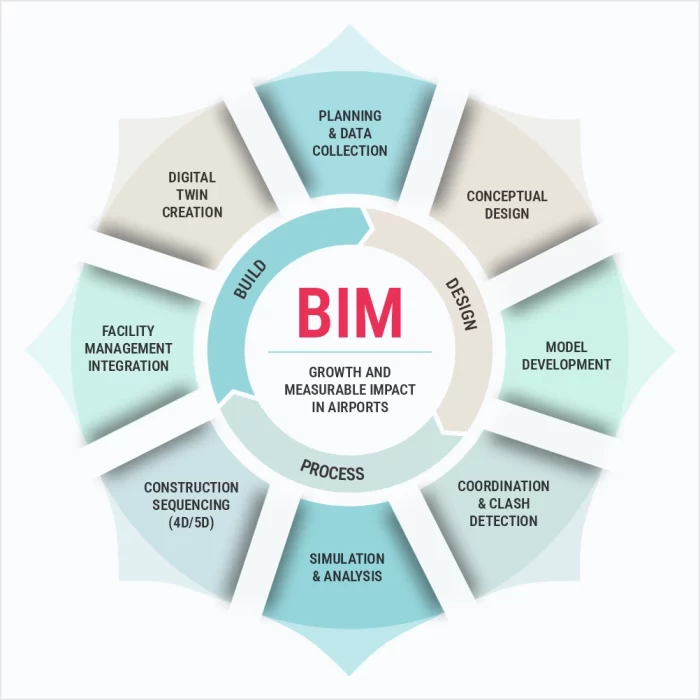
01
BIM for Safety & Risk Management
Airport construction safety is improved by identifying risks early through site simulations and workflow analysis. BIM tools integrated with IoT sensors enable real-time monitoring, alerting workers to potential hazards. BIM for risk mitigation analysis ensures that safety protocols are followed, preventing accidents and reducing downtime.
Tools Used: Safety simulations, real-time safety monitoring, IoT sensor integration for hazard detection, and risk mitigation analysis.
02
BIM for Security Systems Design
The effective integration of security systems in airport construction, such as surveillance, baggage scanning, and access control, is ensured. Passenger flow is simulated to optimize security checkpoint layouts, reducing congestion and improving efficiency. BIM for 3D visualization allows for precise placement and coordination, ensuring smooth operations once the airport is functional.
Tools Used: Security system integration, passenger flow simulations, and 3D modeling for system placement.
03
BIM for Passenger Experience Optimization
Passenger flow is optimized by simulating crowd movement and identifying potential congestion points throughout the airport. This allows for the design of terminal spaces that facilitate smooth transitions, minimize bottlenecks, and enhance overall comfort. By visualizing passenger behaviors, strategic placement of amenities, seating, and security checkpoints is possible, improving both efficiency and satisfaction.
Tools Used: Passenger flow simulations, user-centered design tools, congestion analysis, space utilization modeling.
04
BIM for Sustainability & Green Certifications
Airports can achieve sustainability objectives by simulating energy consumption, optimizing material usage, and designing eco-friendly terminals. This approach supports the creation of green buildings that meet certifications like LEED, ensuring environmentally conscious construction practices.
Tools Used: Energy simulation tools, material optimization analysis, and sustainability modeling.
05
BIM for Maintenance & Facility Management
After construction, the 3D model transitions into a powerful asset management tool, tracking airport systems, equipment, and infrastructure. Integrated with IoT, it monitors real-time performance and predicts maintenance needs, helping reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of airport facilities. This predictive maintenance approach ensures systems remain operational without unexpected interruptions.
Tools Used: Asset tracking, predictive maintenance with IoT integration, real-time performance monitoring.
06
BIM with AR & VR for Enhanced Visualization
BIM integrates with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) to create immersive, real-time visualizations of airport designs. This enhances communication, decision-making, and collaboration among stakeholders, offering a clearer understanding of complex designs before construction begins. AR integration also enables virtual walkthroughs, improving the way stakeholders experience the project.
Tools Used: Virtual walkthroughs, AR overlays for real-world site visualization, immersive 3D modeling.
07
BIM for Digital Twin Technology
When combined with IoT, BIM creates real-time digital replicas of airport infrastructure, called Digital Twins. This innovative technology allows for continuous monitoring, analysis, and optimization of airport operations, enhancing performance and enabling proactive maintenance. Together, BIM and Digital Twin technology greatly improve the long-term management and efficiency of airport facilities.
Tools Used: Digital Twin creation, real-time system monitoring, IoT data integration.
Building Information Modeling is critical to modern airport construction, from the initial design phase to ongoing operations. Its advanced tools ensure safety, boost efficiency, and enable the creation of smarter, more sustainable airports. By integrating innovative technologies, It streamlines workflows and supports long-term operational success.
Real-World Case Studies Of BIM In Airports
- John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), Terminal 5 Expansion
- Utilization: BIM for design visualization, construction sequencing, and operational modeling.
- Changes: Integrated design elements for improved planning and smoother construction.
- Results: The expansion enhanced passenger flow and boosted terminal capacity, all while staying on budget and reducing the risk of delays.
- Sheltair Aviation, FL
- Utilization: BIM for architecture, structural analysis, and MEP system coordination.
- Changes: Facilitated seamless integration between architecture, structural elements, and MEP systems, ensuring alignment across all disciplines from the start.
- Results: Increased project accuracy, minimized design conflicts, and enhanced collaboration among teams, leading to a smoother construction process and timely delivery.
- Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), Tom Bradley International Terminal Expansion
- Utilization: BIM for clash detection, 3D modeling, and project scheduling.
- Changes: Improved system coordination by visualizing mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems.
- Results: The expansion was completed on time and within budget. It minimized rework, enhanced workflow efficiency, and optimized passenger flow, improving terminal capacity.
- Chicago O’Hare International Airport (ORD), O’Hare 21 Modernization Program
-
- Utilization: BIM for systems integration, scheduling, and construction sequencing.
- Changes: Optimized the design and construction phases by coordinating complex airport systems.
- Results: Reduced project delays and costs, leading to improved terminal efficiency and smoother execution. Enhanced collaboration across teams resulted in faster decision-making and reduced rework.
- San Francisco International Airport (SFO), Terminal 1 Renovation
- Utilization: BIM for clash detection, scheduling, and cost estimation.
- Changes: Improved coordination across different construction teams and optimized the flow of materials and resources.
- Results: The renovation was completed ahead of schedule, with significant cost savings. Passenger experience was enhanced with improved flow, and operational bottlenecks were minimized.
- Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta International Airport (ATL), Concourse T Expansion
- Utilization: BIM for real-time monitoring, resource management, and system integration.
- Changes: Enhanced team collaboration through shared data and early risk identification.
- Results: Reduced operational disruptions and achieved cost savings. The integration allowed for quicker identification of potential risks, streamlining the construction process and improving long-term operational efficiency.
- Denver International Airport (DEN), South Terminal Redevelopment Project
- Utilization: BIM for system design coordination, scheduling, and conflict resolution.
- Changes: Facilitated better communication and collaboration between contractors and designers.
- Results: The project saw cost savings and time reductions. It enhanced operational efficiency, providing real-time insights into system integration and improving the overall execution of the redevelopment.
These airports leveraged BIM for a variety of purposes, from system integration to resource management, achieving substantial improvements in cost, time, efficiency, and collaboration across teams.
BIM (Building Information Modeling) integrates data to streamline airport design, construction, and operations, ensuring efficiency and cost savings.
BIM identifies risks early and enhances safety by simulating workflows and integrating IoT sensors for real-time hazard detection.
BIM offers tools that allow airport decision makers to understand all components of a facility—their location, and their attributes, both graphically and systematically—to minimize the total cost of owning and operating an airport facility.
BIM enables accurate cost estimation, helping reduce unexpected expenses and optimizing project budgets for airports.
BIM continues post-construction, aiding in asset management, predictive maintenance, and long-term operational efficiency.
About the Author

Coordination Manager / VDC Manager at United BIM
With over 10 years of experience in the AEC industry, Akash Patel is a seasoned Coordination Manager and VDC Manager at United BIM. His expertise lies in managing complex MEP-FP coordination projects and leveraging cutting-edge BIM technology to ensure seamless collaboration and precision. Akash is dedicated to delivering high-quality, detailed models that meet the demands of modern construction. He is passionate about optimizing workflows and driving innovation within the BIM field.